Izotope Rx Manual Pdf Español
Mar 25, 2015 Give your final mix a quick “shine” and “polish” in our creative mastering platform Ozone using these 10 simple steps. Download your free, 10-day trial: http. IZotope Software & Plug-ins Click here for all support articles.
| Module & Plug-in |
|---|
SelectionTools 50 SelectionModifiers(PC/Mac) 53 RXModules 58 WorkingwithRXApplicationModules 59 WorkingwithRXPlug-Ins 65 RepairModules&Plug-Ins 76. Introduction Here at iZotope, we specialize in building audio products for music production, post production and broadcast. The RX Plug-in Pack is a collection of the four essential plug-ins from the RX. Sep 14, 2018 Video 1 of 28 for iZotope RX 7 301: RX 7 - The Unofficial Video Manual Its no secret that iZotope RX is the king of audio repair. IZotopes cutting-edge spectral processing software is by far the. Serato pro dj crack code.

Overview
De-hum is designed to remove persistent tonal noise, like the AC hum that can be caused by poor electrical grounding. De-hum includes a series of notch filters that can be set to remove both the base frequency of the hum, usually 50 Hz (Europe) or 60 Hz (USA) as well as any harmonics. The De-hum module is effective for removing hum that has up to seven harmonics above its primary frequency.
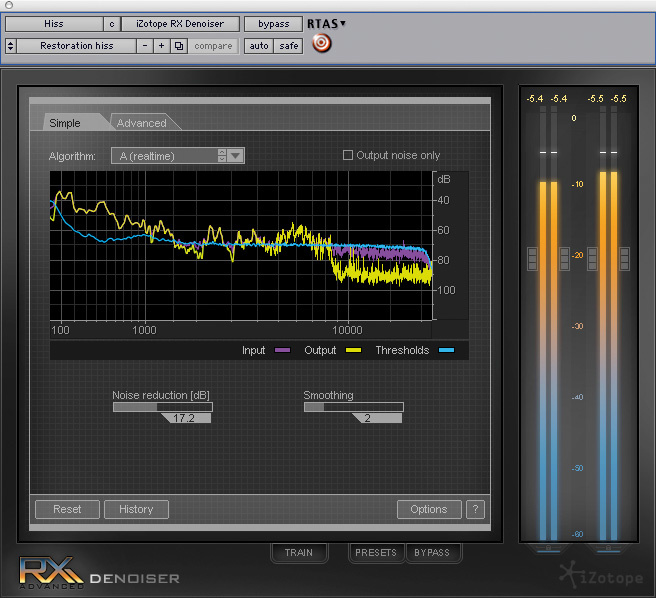
Controls
If RX 5 Audio Editor has been downloaded directly from iZotope or another re-seller, the serial number will be emailed to you, along with the link to download the product. IZotope RX 2 Help Documentation 10 Interface Here is a general overview of RX's main workspace. It's a good idea to familiarize yourself with this window before moving on. RX's interface is design ed to give you a full range of tools for repairing audio. In addition to its processing modules, RX provides a.
- BASE FREQUENCY: Sets the fundamental frequency of the hum to be removed. The Free option unlocks the Notch Frequency control and allows you to manually identify the fundamental. With Preview engaged, adjust the slider until you find the point where the hum is appropriately reduced.
Tip
You can also use the Spectrum Analyzer to help identify the base frequency of the hum.
- SUGGEST: De-hum can intelligently identify the noise profile of the hum in your audio. Make a selection containing the hum in isolation, and click the Suggest button. This will automatically set the Base Frequency based on the learned profile. If you cannot find a selection of hum in isolation, RX can analyze any audio with prominent hum, but the results may not be as useful.
- ADAPTIVE MODE: Allows De-hum to adjust the notch filters based on changes in the audio over time. In this mode, RX will analyze incoming audio to determine what is hum and what is desired audio material. Adaptive mode will work better with hum that changes in pitch throughout the file.
- FILTER Q: Controls the bandwidth of the notch filters for the base frequency and all of the harmonics.
LINEAR-PHASE FILTERS: Linear-phase enables FIR (Finite Impulse Response) filters with a high FFT size. These filters provide very accurate frequency response with no change in phase at the expense of latency and filter pre-ringing.
Disabling Linear Phase (FIR) filters
- When Linear Phase is disabled, De-hum will use minimum-phase IIR filters. These are also very accurate, and are only susceptible to post-ringing, which is usually less noticeable than the pre-ringing introduced by FIR filters.
- Latency Consideration: Disabling Linear Phase Filters will reduce the latency used by De-hum when it is being used as a real-time plug-in.
- When Linear Phase is disabled, De-hum will use minimum-phase IIR filters. These are also very accurate, and are only susceptible to post-ringing, which is usually less noticeable than the pre-ringing introduced by FIR filters.
HIGH/LOW-PASS FILTERS: These traditional filters come ahead of the De-hum notch filters, and allow for frequencies to pass above or below a certain cutoff point. These can be useful for tackling extreme hum or buzz.
- FREQUENCY [Hz]: sets the cutoff frequency for the filter
- Q: Sets the bandwidth of the filter (or dB/octave cut). In the default IIR filter mode with a high Q setting, you may notice a resonance at the cutoff frequency characteristic of traditional analog filters. That resonance can be mitigated by engaging the Linear-phase filters.
- FREQUENCY [Hz]: sets the cutoff frequency for the filter
NUMBER OF HARMONICS: Because harmonics often accompany the fundamental frequency of a hum, De-hum can also attenuate these overtones with notch filters. Using the Number of Harmonics control, you can select up to 7 harmonics above the fundamental. The spectrogram display can make it easy to identify the harmonics. After selecting the number of harmonics, use the Slope control to set how aggressively the higher harmonics are attenuated.
LINK HARMONICS: Connects the gain controls of the notch filters.
- ALL: presents a single node on the display for controlling the gain of all the notch filters. This is the default setting.
- ODD/EVEN: presents two nodes on the display, one for controlling the gain of the fundamental frequency and even harmonics, and another for controlling the 1st harmonic and any following odd harmonics.
- NONE: presents individual gain nodes for the fundamental and each harmonic.
- ALL: presents a single node on the display for controlling the gain of all the notch filters. This is the default setting.
SLOPE: When harmonics are linked, this controls the harmonic slope of the gain nodes for each overtone. As the harmonic order increases, the gain level resolves closer to 0 dB. When the Link Harmonics control is set to Odd/Even, a separate control appears that affords independent control over the slope for both odd and even harmonics.
HARMONIC GAINS [dB]: This section provides a numerical readout of the notch filter gain settings in decibels. You can also manually enter gain settings for the fundamental, or any of the harmonics if Link Harmonics is set to None.
FILTER DC OFFSET: This checkbox will engage a filter to remove any DC (direct current) offset that sometimes occurs in A/D converters or analog circuits used in the recording process.
OUTPUT HUM ONLY: Selecting this check box will isolate the hum that is being removed. This is useful for fine-tuning your settings. Identify a section of your file where the hum is mixed with other material, select this mode, and click Preview. Now adjust parameters like Filter Q and Slope control to maximize hum removal, thus minimizing the effect on the program material.
More Information
Alternative Modules to use for Complex Hum Issues
- Spectral De-noise For hum that has many harmonics that extend into higher frequencies (often described as “buzz”), try using Spectral De-noise. Spectral De-noise features tonal noise reduction controls that can make short work of harmonic hum and buzz across the entire spectrum.
- De-click Some very high frequency buzz can also be removed with the De-click module.
Visual Example
This image shows the spectrogram of a file with 3 harmonics of a 60 Hz Hum:
That said, RX 7, the latest version of the toolkit, also boasts various features that make it a powerful asset for commanding and elevating musical performances. Whether you’re working with post production or music production, this feature guide will overview some of the essential components that you’ll want to be aware of to get the most out of RX 7 Standard.
Overview
RX 7 Standard has two primary components: the standalone RX Audio Editor, and a collection of plugins that can be used right within your DAW. We’re going to focus primarily on the standalone editor, which hosts some of the most powerful functionalities RX 7 Standard has to offer (and also includes all of the individual plugins).
When you open up the editor, you’ll be greeted by a blank slate that looks something like this:
To get started, select an audio file from your computer using the “Open File” button, or simply drag and drop it right into RX 7 Standard. Up to 16 audio files can be opened at a time, so feel free to work on many different audio files in parallel. Once an audio file is loaded up, the GUI will display a spectrogram representation of your waveform:
Pro Tip: Want to see a standard waveform rather than a spectrogram display (or a little bit of both)? Use the slider on the bottom left of the GUI to adjust the waveform / spectrogram opacity:
This is the basic setup for using RX 7 Standard – you can now begin editing and enhancing your audio using the modules accessible via the right-hand bar. Though we won’t go through all of them, we’ll highlight some key components – starting with Music Rebalance.
Music Rebalance
One of the biggest new features introduced in RX 7 Standard is Music Rebalance, an intelligent tool that employs a machine learning-trained algorithm to identify voice, bass, percussion and other individual components within a greater mix. With Music Rebalance, a mix can be adjusted and re-animated regardless of whether you have the stems at hand. Subtly boost your bass and percussion, or fearlessly isolate or remove vocals from a track according to your needs.
Once you click on the Music Rebalance feature, it’ll open up a separate window that looks something like this:
Let’s explore some of the adjustable parameters in greater detail:
- Gain adjusts the dB level of the particular component (voice, bass, percussion, or other).
- Sensitivity sets how strict the separation algorithm will be in defining what it considers to be a particular type of sound. Low values will contain less bleed in exchange for more artifacts, while higher values will contain more bleed in exchange for less artifacts. Note that the sensitivity values are relative to one another, meaning that setting all values to 3.0 is the same as setting all values to 9.0.
- The separation algorithm determines how the module separates the sound sources, and can be set to channel independent,joint channel, or advanced joint channel mode. The channel independent mode offers the fastest but lowest quality separation, while the advanced joint channel mode takes more processing time but offers the highest quality separation.
Pro Tip:Each setting you create can be previewed, bypassed, compared, and rendered. Consider previewing a lower quality demo before comparing, since the latter can take some time to load. That said, the compare function is extremely helpful for experimenting with and A/Bing different sensitivity and gain settings before choosing one to render.
Repair Assistant
Another significant addition brought to RX 7 Standard is Repair Assistant, a feature that detects noise, clicks, sibilance, and more so that you can clean up your audio with more efficiency and effectivity than ever. You can access this intelligent helper by pressing Repair Assistant button on the top right corner of the application. This will initiate a menu that prompts you to identify a material type – dialogue, music, or other:
Once you select the appropriate source and hit “Start analysis,” Repair Assistant will begin analyzing your audio for issues in clipping, clicks, hum, and noise:
Pro Tip: Confident that your audio already sounds great? If Repair Assistant doesn’t find any issues in these categories, it will still generate some subtle cleanup processing chains for you.
Rx 7 Izotope
After its analysis, Repair Assistant offers you three possible solutions with 10 second previews that can be easily compared and contrasted against the original audio:
Pro Tip: Use the intensity variant buttons (right below each preview spectrogram) to generate two additional intensity variations of a single processing chain:
De-bleed, de-ess, de-plosive, de-X
One of the first things you may have noticed about RX 7 Standard is how many ‘de-somethings’ occupy the list of modules:
It accompanies a limit of 4 playback decks, up to 32 impacts to give your blends an individual touch, a four-channel blender and test decks for live remixing. The rich documentation area gives stretched out help manuals to facilitate the way toward understanding the product use.Traktor flaunts an amicable situation, with jazzy multicolor cushions and TruWave shaded waveforms to guarantee an animating visual ordeal. Traktor pro no sound effect. Proficient DJs ought not to think that its difficult to figure out how to utilize it, despite the fact that amateurs could invest a significant measure of energy unwinding its highlights and conduct.
Iphone Manual Pdf
Most of these features address the need to attenuate something undesirable that was captured in a recording, and their parameters are pretty straightforward. Let’s just quickly outline what each module targets:
- De-bleed attenuates the leakage of one signal into another, most commonly used to combat microphone and headphone bleed.
- De-click eliminates undesirable short impulses that are often the result of digital errors, mouth noises, etc.
- De-clip removes digital and analog clipping artifacts, particularly useful for salvaging one-take recordings that would be perfect if not for a moment of clipping.
- De-crackle removes clicks that are close together in time and soft in volume, great when utilized in conjunction with de-clip.
- De-ess attenuates sibilance, most commonly used with vocal recordings.
- De-hum targets and eliminates stable tonal noises, often caused by air conditioners or other electrical appliances.
- De-plosive reduces plosives in a signal, particularly handy if a pop filter was not utilized during the recording process.
- De-reverb allows you to control the amount of ambient space in a recording, using signal analysis techniques to propose optimal setting suggestions.
Depending on whether you’re doing post production, dialogue editing, music production, or something else altogether, you may find that you use some of these modules more than others. What’s key is learning to identify what issue is present in your signal, and then finding the tool that addresses your particular issue (and for many of the most common problems, Repair Assistant is there to help you out). The above modules are all available as plugins too, which means they can be quickly accessed directly within your DAW.
This concludes our tour of RX 7 Standard’s key features – there’s so much more to explore with the toolkit, but hopefully this guide gives you some starting points for you to get your feet wet. If you have a question, leave it in the comments below.
September 13, 2018